
- ·收藏本站

前言
什么是APRS
APRS是英文“Automatic Packet Reporting System”的缩写,中文译为“自动分组报告系统”。这个名称是发明者Bob Bruninga,WB4APR的注册商标。名称中所指的内容可能会让新手困惑。
首先,APRS是一个通信协议。它定义了数据(包括电台和地图物体位置、气象信息、无线电测向、文字信息和遥测)如何通过无线电分组电台通信。
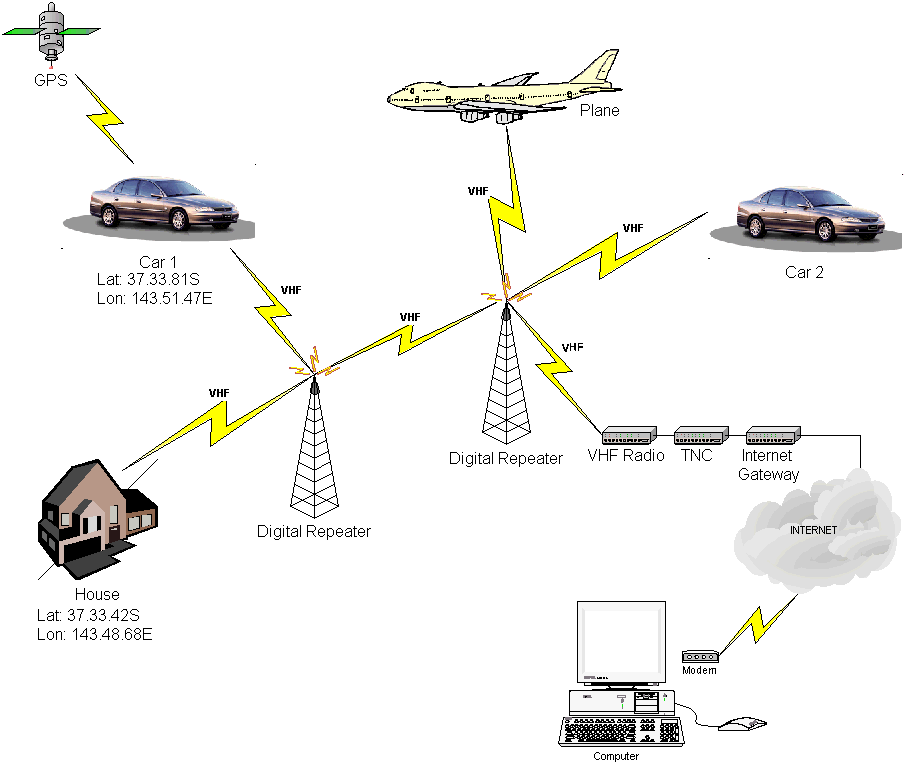
APRS也指包含APRS信息的网络。贯穿美国,欧洲和一些其他的国家,一个数字中继(“digipeaters”)网络,通常工作在一个共同的全国性的频率,为APRS分组提供传输。通常大部分APRS电台工作在其中一个通常的频道,但是不绝对。
APRS互联网系统(APRS-IS)是一个基于互联网的附属于电台的网络。互联网网关(IGate)通常就是一台能访问互联网的家庭PC和一部电台。网关将电台网络的流量传送到一个共享的、世界范围的APRS流。许多IGate至少会传送文本信息流,一些时候也会传送其他信息。从互联网将数据传回电台网络。用这种方法,文字信息可以从一个电台传递到另一个电台。甚至两个电台间不存在中继器或不在一个中继器的覆盖范围内。
APRS的名称有时候指WB4APR原始的MS-DOS APRS地图程序。但是这个程序现在正确的叫法是APRSdos。目前有数种地图和消息程序存在,使用APRS电台网络或APRS-IS,或者两者均用。一些程序同样拥有IGate功能。
连接到世界范围的APRS-IS流是许多数据库服务。这些系统(findu.com和aprsworld.net是两个最受欢迎的系统)处理、存储所有的APRS数据流,按照转发规则将数据转发到世界上任何一个IGate。大多数系统提供地图、天气显示、基于流量的地遥测图。这个功能允许任何人通过互联网访问监视APRS数据而不需要电台设备或特殊的软件。
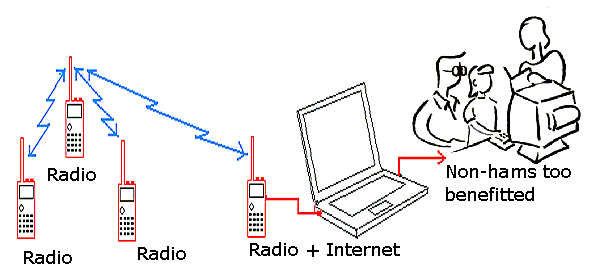
当然,将数据上传到web连接的数据库并不是APRS唯一的好处。依靠网络的覆盖和负载,仅使用电台网络完成数百英里范围内通讯覆盖也是可能的。但是,在一个共享网络中伴随着中继器的增加,系统可靠度降低。APRS 最可靠的级别是地区级(LOCAL LEVEL),所以在一个地区使用多于两个或三个数字中继是不明智的。通常情况下,使用一个中继器是最适合本地覆盖的。
APRS协议、硬件、软件可以独立的使用在国家级网络上。本地或临时网络可能因为特殊事件或满足特定组织需要而建立。一些应用可能不需要数字中继。例如高空气球经常使用APRS将位置和遥测数据通过一个专用频率直接发送到搜寻队。
移动使用APRS可以有多种不同的形式。最简单移动APRS设置是一个仅具有发射功能的追踪器连接一部电台和一个GPS 接收机。这些追踪器通常没有接收功能,除了在发射前追踪器会检测频道是否被占用。追踪器允许自己的车辆被他人追踪,但是无法接收信息或者位置。
另外一种选择是一部具有APRS功能的电台,例如Yaesu vx-8R,FT-1D。这些电台有一个文字显示屏,但是需要一部带有地图功能的GPS接收机显示位置和其他电台。
一部普通电台配合TNC与一部笔记本电脑或PDA结合使用可以提供完整的APRS功能。包括地图定位、消息功能。虽然这通常是最贵的配置而且在驾驶的过程中操作不方便。
用简易图示说明如下:
目前APRS系统使用的频率有公约划定,亚洲中国分配频率是144.640MHZ,当然也可以使用任何其他业余频率,甚至是HF,这样可以有更广泛的电波覆盖。
搭建APRS系统的基础条件有哪些?
一些相关的客户端软件:
| Software Name (and link) |
OS(es) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| APRSdos | MS-DOS | The original APRS application. Specialized versions are also available. While not directly APRS-IS capable, it sets the standard for APRS packets. |
| AFilter | Windows (32 bit) |
Data stream filter application. |
| AGWTracker | Windows (32 bit) |
GUI with multiple map types. |
| AGWTrackerPPC | Windows Mobile | GUI for Windows Mobile |
| ALogger | Windows (32 bit) |
APRS-IS logging application. |
| APRSISCE/32 | Windows Mobile, CE Windows 32 and 64 bit |
GUI client for Windows Mobile and Windows 32 & 64 bit OSes |
| APRS/CE | WindowsCE | GUI client for Windows CE |
| APRSPoint | Windows (32 bit) |
GUI client. Uses MapPoint for maps. |
| Aprsg | Linux, Windows | IGate |
| APRS-Go | Windows Mobile | GUI client for Windows Mobile |
| Aprx | UNIXes, Linux, BSD, Sunos | APRS Rx IGate and digipeater supports Linux AX.25 and serial interfaces. |
| APRS+SA | Windows (32 bit) |
GUI client and IGate. Uses Street Atlas for maps. |
| javAPRS | Java Applet | GUI applet for web pages. |
| mAPRS | Java Midlet | Midlet for Mobile Devices. |
| MacAPRS | MacOS | GUI client and IGate |
| Packetograph | MacOS | GUI client |
| pocketAPRS | PalmOS | GUI client for Palm OS. NO LONGER AVAILABLE OR SUPPORTED (I am not the author of this software) |
| SARTrack | Windows (32 bit) | GUI designed for Search and Rescue, Tactical callsigns, multi-colour tracks, Search Areas, Messaging, SAR Logging |
| SmartPalm | PalmOS | Text client. |
| UI-View | Windows (16 & 32 bit) |
GUI client and IGate. |
| WinAPRS | Windows (16 & 32 bit) |
GUI client and IGate |
| X-APRS | Linux | X-Windows GUI client and IGate |
| XASTIR | X-Window OSes (Linux/Unix/MacOSX) |
GUI client and IGate. |
| YAAC | Windows (32 & 64 bit) Mac OS X, Linux, FreeBSD |
GUI client and IGate |
问答:
Q:手机能够使用APRS服务吗?
A:目前有支持智能手机的软件,可以用手机使用APRS服务,在使用之前需要先用业余无线电呼号注册并取得验证码,注册地址http://www.apritch.myby.co.uk/uiv32_uiview32.php?lang=english;大约在48小时内获得验证码,获得验证码后下载智能手机软件来使用服务;
1、Adroid手机:在这个地址下载软件http://aprsdroid.org 或者扫描下方二维码;有些同学说第二外语是日语、法语、俄语…唯独没有学习英语,那我给出更具体的下载地址:http://aprsdroid.org/download/ 如果还找不到,那就直接下载这个http://aprsdroid.org/download/APRSdroid-current.apk
联机地图版下载:APRSdroid-gl-2015-04-03.apk
脱机地图版下载:APRSdroid-gl-2015-03-28_osm_nojit.apk
脱机地图包下载一:China.map(境外网站有可能被限制!!!)
脱机地图包下载二:百度网盘下载:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1c06gIUs 密码: svvr
BTW:脱机地图包下载后,更名为aprsdroid.map,然后复制到SD卡根目录下。安装脱机地图版的APRSdroid就会自动调用SD卡根目录下的地图文件了。
安卓版中文免费Aprs软件:流云安卓版,百度网盘下载: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eQ6IBAi 密码: 48jf
安卓版注册收费的中文Aprs软件可以下载http://www.aprsmap.org/downloads/app/APRSMap_Focus_1.0.2.apk
2、iOS系统:OpenAPRS on the App Store on iTunes
3、WindowsMobile系统:http://www.aprsgo.com
4、WindowsPhone系统:待测试…
5、PC软件
KComm is a logging and CW / data communication program for the Elecraft K2 and K3 transceivers that is available for both Microsoft Windows and Linux.
VOAProp was written to satisfy my needs for a program that would show me what HF band propagation should be like on a particular day on a particular band.
Morse Machine is one of the best tools ever for learning to read Morse at a good speed. It teaches Morse code using a tried and tested technique called the Koch Method.
MorseGen is a program that can generate Morse Code for practice purposes. It can be used to teach yourself Morse using the Koch Method and can generate audio files which can be played on a CD player or MP3 player.
MorseTest is a Morse Code proficiency builder that is loosely modelled on a CW contest. It’s the most fun way to improve your Morse proficiency that I know of.
K2Net is intended to allow remote operation of an Elecraft K2 across a network.
KTune is a small utility that allows you to use a Griffin Powermate USB knob to tune your Elecraft K3 radio. It should work with a K2, too!
PSK31Test is a demonstration of how to use the PSK31 Core DLL written by Moe Wheatley, AE4JY, in a Borland Delphi program.
Q:为什么部分安卓手机无法使用APRS软件?
A:但凡玩aprs的安卓手机拥有者,都曾遇到安卓aprs软件无法安装的窘境。罪魁祸首就是缺少谷歌包(当然必须root后),安卓2.3和4.0的发上来,方便大家。2.3谷歌包 http://pan.baidu.com/s/1u06y5 ;4.0谷歌包 http://pan.baidu.com/s/18DHor(注:卡刷包,无需解压,直接放到内存卡根目录,进行卡刷。详细这里不解释,请绕道度娘)
Q: 我想更换APRS登录服务器,具体IP那里查询?
A:请参考如下地址获取:
Intro: http://www.aprs-is.net
Tier 2 Network: http://www.aprs2.net/
Tier 2 Network Server Monitor: http://www.aprs2.net/mon.htm
Tier 2 Server List: http://www.aprs2.net/APRServe2.txt
前言:aprs的符号用字母代替,但是有两个页面的符号可以选择,两个页面分别是 / 和 \每页选取相应的字母,就是aprs设备的移动标识符号,例如汽车在图 / 中,对应字母是 >
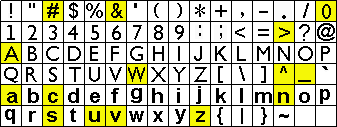
符号页“/”
符号页“\”
相关技术文档下载:APRS_Symbol_Chart
区别不同的台站设备或者类型:
-0 家庭电台和运行因特网网关的家庭电台iGate(通常家庭电台不使用SSID)
-1 数字中继,运行RELAY中继的家庭电台和气象数字中继台
-2 UHF数字中继DIGI
-3 独立的VHF数字中继DIGI,例如架设在山上
-4 HF到VHF网关
-5 因特网网关iGate(非家庭电台)
-6 用于卫星操作
-7 建伍TH-D7等手持便携APRS电台
-8 用于船、帆船和舰船等
-9 用于移动电台
-10 用于只使用Internet的操作
-11 用于APRS touch-tone用户(偶尔用于气球)
-12 便携单元,例如笔记本电脑、手机、野营地等
-14 用于卡车移动操作
-15 用于HF
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
|
APRS SSID Recommendations 6 Feb 2012---------------------------------------------------------------------Updated 6 Feb 2012 to clarify the title of this document to be SSID RECOMMENDATIONS not to imply any kind of decoding "standard". That original NMEA decodign standard is covered in the original specUpdated 9 June 2010 for more flexibility using 1,2,3,4 and 15Revised 2 June 2004 to add -10, -11, 12 and -15SSID's have seen two different uses in APRS. Initially as an ICONindicator back in the early 1990's. But that is obsolete for overa decade. Now SSID's are used as an informal way of indicating one of several different typical APRS applications.Since many small displays for the handheld and mobile operator shownearby APRS station callsigns that flash up on the screen, it is niceto have some idea of what type of station or activity might be involved simply from the callsign SSID without having to push buttons, search lists, or look at maps to find out more about them. SSID RECOMMENDATIONS: It is very convenient to other mobile operators or others looking at callsigns flashing by, to be able to recognize some common applications at a glance. Here are the recommendations for the 16 possible SSID's (the limit of 16 comes from the 4 bits available in the AX.25 protocol. Note, The SSID of zero is dropped by most display applications. So a callsign with no SSID has an SSID of 0.-0 Your primary station usually fixed and message capable-1 generic additional station, digi, mobile, wx, etc-2 generic additional station, digi, mobile, wx, etc-3 generic additional station, digi, mobile, wx, etc-4 generic additional station, digi, mobile, wx, etc-5 Other networks (Dstar, Iphones, Androids, Blackberry's etc)-6 Special activity, Satellite ops, camping or 6 meters, etc-7 walkie talkies, HT's or other human portable-8 boats, sailboats, RV's or second main mobile-9 Primary Mobile (usually message capable)-10 internet, Igates, echolink, winlink, AVRS, APRN, etc-11 balloons, aircraft, spacecraft, etc-12 APRStt, DTMF, RFID, devices, one-way trackers*, etc-13 Weather stations-14 Truckers or generally full time drivers-15 generic additional station, digi, mobile, wx, etc* One-way trackers should best use the -12 one-way SSID indicatorbecause the -9's usually mean a ham in full APRS communicationboth message and voice. The -9's can be contacted by APRS messageor by Voice on his frequency included in his beacon, or on VoiceAlert if he is in simplex range. The -12's are just moving Iconson the map and since they have no 2 way communication for ham radiothey are not generally of routine interest to other operators.OBJECTS or INTERNET: In addition, Objects or internet generated stations can have any SSID, not just the original 16, since Objects are not constrained by the AX.25 header and can have a 9 byte name. Here are some common OBJECT/Internet SSID's:-63 for PSK63 HF stations-tt for APRS TouchTone users (DTMF)-ID for RFID-A through -Z for DstarSSID BACKGROUND: Originally, in 1992, we had to use the SSID asa way of indicating the type of station that transmitted a raw NMEA-0183 GPS sting. But in the mid 1990's we began indicating any of the nearly 200 APRS symbols by the setting of the AX.25TOCALL of "GPSxyz". The "xyz" characters define the symbol from the standard APRS symbol table www.aprs.org/symbols.html.The GPSxyz concept worked so well, the original SSID associations are no longer a required part of the spec. But the conventionsthat evolved from those early SSID's are still encouraged asnoted above, for easy recognition of station type or activity by when only the callsign is seen.The -1, -2, -3, -4 and -15 are kept generic so that anyone withas many as 6 digipeaters, or 6 trackers or 6 weather stations or6 vehicles can still have unique SSID's for each of his stations.Beyond 6, people will just have to use any SSID that suits theirfancy. In some areas there might be 15 digipeaters all underone guy's call!SSID USAGE: The SSID's also might give a hint as to how someone is getting into APRS whether via satellite, a one-way tracker, a mobile, an HT or even via DTMF or an RFID device or whether he isdoing something special.For example, if you are doing something special, change your SSID to -6 to alert others to your excitement, or to make thetrack-history begin and end on site, and not be tied to all your other -9 travels. Or use -6 SSID for a packet sent via the ISS or APRS satellite or for a 6 meter test so thesuccessful packet is preserved and not overwritten by the sameradio the next time you use it not via the ISS on the 144.39national channel. By using separate SSID's the WEB data bases will keep statistics and data separate from when you are working normally on other bands with other SSID's.So stick to the suggestions above for the obvious applications where you can. Of course these are not rigid. If you have more than 6 digipeaters, use any SSID you want. These are only guidelines to hint at a station's possible application when all you can see easily is the callsign on a screen or in a list....de WB4APR, Bob |